 可视化处理方案
可视化处理方案
两个实际开发中最常用到的数据可视化类库:
利用这两个库我们将会实现 6 块图表:
- 累计收益:柱状图 + 曲线图
- 日金额分析:横向柱状图(正负)
- 大区营销图示:饼图
- 关键云词:文档云图
- 营收业绩图示:百度地图 +
echarts的散点图 - 大区营销数据分析:表格数据分析图
额外配合 其他类库 或 element-plus 组件 来实现 各种数据联动 的效果。
# 数据可视化大解析
- 数据可视化场景
- 数据可视化常见解决方案
- 不同场景下解决方案是否具备通用性
# 数据可视化场景
根据业务来进行划分,在我们实际工作中,常见的可视化场景主要分为两种:
大屏可视化:通常以一个单独的项目进行呈现,主要的目的是:把大量的数据以图表的形式在大屏中进行展示。
数据可视化:不以单独的项目进行呈现,通常被集成在后台系统之中。主要的目的是:把大量的数据以图表的形式在小屏(通常为普通电脑屏幕)中进行展示。
# 常见解决方案
数据可视化其实核心就是:通过图表展示数据
所谓 数据可视化解决方案 指的其实就是:通过图表展示数据的解决方案
所以对应的核心就是:如何构建图表 。
目前常见的数据可视化图表,主要有三个:
- Apache ECharts (opens new window):由 Apache软件基金会 (opens new window) 提供,前身是百度
Echarts。提供了PC端和 移动端 的各种图表处理,应该也是大家最为熟悉的一个可视化图表库。 - AntV (opens new window):由蚂蚁集团数据可视化团队发布,内部进行了库的细分:
- G2 (opens new window):类似于
Echarts,提供了各种常见的图表 - S2 (opens new window):表格数据图形化,课程中的 大区营销数据分析 ,就是基于此实现
- G6 (opens new window):数据关系可视化。比如脑图实现
- X6 (opens new window):图形编辑引擎。比如流程图、
ER图构建 - L7 (opens new window):地理空间数据可视化。与地图相关
- F2 (opens new window):移动端数据可视化。可以理解为
G2的移动端版本 - AVA (opens new window):可视化生成框架。可以理解为可视化的低代码框架
- G2 (opens new window):类似于
- highcharts (opens new window):可以理解为另一个团队开发的
Echarts,应用层中与Echarts相比,并无明显特点。
# 不同场景下解决方案是否具备通用性
无论是 大屏可视化 也好,数据可视化 也好,ECharts 也好,AntV 也好。本质上都绕不开这样的一个核心理念。
所以我们只需要掌握:如何根据数据,利用框架来绘制图表 这样的一个核心解决方案即可。在不同的业务场景中,我们只需要处理对应的不同业务就可以了。
# 构建基础模块结构
- 在现有的路由表之中,新增一个 公开路由
chart,表示咱们的数据可视化模块 - 处理
chart组件的基本结构,划分出各个图表的区域
# 新增 chart
新建
src/views/chart/index.vue组件在
src/router/index.js中新增公开路由表:{ path: '/chart', name: 'chart', component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "chart" */ '@/views/chart/index'), meta: { title: 'chart', icon: 'chart' } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 处理基本模块
点击查看
根据以下结构,分别创建对应的图表模块:
.assets/image-20220617170835377.png)
对应模块分别为:
- 第一行:
- 累计收益趋势图(
286px):src/views/chart/components/trend/index.vue
- 累计收益趋势图(
- 第二行:
- 日金额分析图(
443px):src/views/chart/components/horizontal-bar/index.vue - 日历图(
443px):src/views/chart/components/calendar/index.vue
- 日金额分析图(
- 第三行:
- 饼图(
240px):src/views/chart/components/pie/index.vue - 文档云图(
240px):src/views/chart/components/word-cloud/index.vue - 地图可视化(
500px):src/views/chart/components/b-map/index.vue
- 饼图(
- 第四行:
S2表格数据图示(804px):src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/index.vue
- 第一行:
完成每个模块的基本初始化:
<template> <div class="container">模块名字</div> </template> <script setup></script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { height: 对应模块高度; background-color: #bcbfc3; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12在
src/views/chart/index.vue中导入各个模块,并构建样式:<template> <div class="chart-container"> <!-- 累计收益趋势图 --> <trend-vue></trend-vue> <!-- 第二行 --> <el-row class="mt-20" :gutter="20"> <el-col :span="16"> <!-- 日金额分析图 --> <horizontal-bar-vue></horizontal-bar-vue> </el-col> <el-col :span="8"> <!-- 日历图 --> <calendar-vue></calendar-vue> </el-col> </el-row> <!-- 第三行 --> <el-row class="mt-20" :gutter="20"> <el-col :span="6"> <!-- 左侧内容 --> <div class="chart-map-left"> <!-- 饼图 --> <pie-vue></pie-vue> <!-- 文档云图 --> <word-cloud-vue class="mt-20"></word-cloud-vue> </div> </el-col> <el-col :span="18"> <!-- 地图可视化 --> <b-map-vue></b-map-vue> </el-col> </el-row> <!-- S2 表格数据图示 --> <table-sheet-vue class="mt-20"></table-sheet-vue> </div> </template> <script setup> import trendVue from './components/trend' import horizontalBarVue from './components/horizontal-bar' import calendarVue from './components/calendar' import pieVue from './components/pie' import wordCloudVue from './components/word-cloud' import bMapVue from './components/b-map' import tableSheetVue from './components/table-sheet' </script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .mt-20 { margin-top: 20px; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# 累计收益-模块划分
在 src/views/chart/components/trend/index.vue 中,构建出左右两个模块,分别用来渲染:
- 数据模块
- 图表模块
具体代码如下:
创建
src/views/chart/components/trend/trend-chart.vue创建
src/views/chart/components/trend/trend-data.vue在
src/views/chart/components/trend/index.vue构建基本结构:<template> <el-card class="container"> <el-row :gutter="32"> <el-col :span="6"> <trend-data-vue :data="chartTrendData" /> </el-col> <el-col :span="18"> <trend-chart-vue :data="chartTrendData" /> </el-col> </el-row> </el-card> </template> <script setup> import trendDataVue from './trend-data.vue' import trendChartVue from './trend-chart.vue' </script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { height: 286px; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 累计收益-数据模块渲染
点击查看
结构划分完成之后,接下来我们渲染 trend-data 数据模块,该模块的基础渲染并不复杂,获取数据直接渲染即可。
创建
src/api/chart.js模块:import request from '@/utils/request' /** * 获取累计收益明细 */ export const getChartTrend = () => { return request({ url: '/chart/trend' }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10因为该数据将会在
chart和data中都被使用,所以我们在src/views/chart/components/trend/index.vue获取该数据:<script setup> ... import { getChartTrend } from '@/api/chart' import { ref } from 'vue' const chartTrendData = ref({}) const getChartTrendData = async () => { const res = await getChartTrend() chartTrendData.value = res } getChartTrendData() </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12在
template中控制 获取到数据之后进行渲染<el-row :gutter="32" v-if="chartTrendData.allAmount">1把数据传递给
trend-data-vue:<trend-data-vue :data="chartTrendData" />1在
trend-data-vue中接收数据并进行渲染:<template> <div class="trend-data-container"> <!-- 累计盈利 --> <div class="title"> <div class="title-name">{{ $t('msg.chart.trendDataTitle') }}</div> <div class="title-amount"> ¥ <span>{{ data.allAmount }}</span> </div> </div> <!-- 今日新增 --> <div class="item"> <div class="item-name item-name-border-1"> {{ $t('msg.chart.trendDataTadayAdded') }} </div> <div class="item-amount"> <span class="item-amount-number">{{ data.tadayAdded }}</span> {{ $t('msg.chart.unit') }} </div> </div> <!-- 今日支出 --> <div class="item"> <div class="item-name item-name-border-2"> {{ $t('msg.chart.trendDataTadayExpend') }} </div> <div class="item-amount"> <span class="item-amount-number">{{ data.tadaySub }}</span> {{ $t('msg.chart.unit') }} </div> </div> <!-- 今日结余 --> <div class="item"> <div class="item-name item-name-border-3"> {{ $t('msg.chart.trendDataTadayBalance') }} </div> <div class="item-amount"> <span class="item-amount-number">{{ data.tadayAmount }}</span> {{ $t('msg.chart.unit') }} </div> </div> </div> </template> <script setup> import { defineProps } from 'vue' defineProps({ data: { type: Object, required: true } }) </script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .trend-data-container { .title { padding: 12px 20px; background: linear-gradient(to right, #0ea5e9, #6366f1); border-radius: 5px; color: white; .title-name { font-size: 12px; font-weight: bold; } .title-amount { font-size: 24px; margin-top: 4px; } } .item { display: flex; justify-content: space-between; align-items: center; border-bottom: 1px solid #c9c9c9; padding: 16px 0; color: #666; .item-name { font-size: 12px; padding: 4px 0 4px 8px; } .item-amount { font-size: 12px; .item-amount-number { color: #333; font-weight: bold; font-size: 20px; } } .item-name-border-1 { border-left: 6px solid #409eff; } .item-name-border-2 { border-left: 6px solid #e6a23c; } .item-name-border-3 { border-left: 6px solid #67c23a; } } } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
# countup - 让你的数据动起来
我们期望让数字以动画的形式进行展示。
安装 countUp (opens new window):
npm i --save [email protected]1countUp (opens new window) 的使用非常简单,我们只需要
new CountUp(target, data, options),得到实例触发start方法即可:<script setup> import { CountUp } from 'countup.js' import { onMounted, ref, defineProps } from 'vue' .... // 本月累计收益(万元) const titleAmountTarget = ref(null) // 今日新增收益 const tadayAddedTarget = ref(null) // 今日新增支出 const tadayExpendTarget = ref(null) // 今日结余 const tadayBalanceTarget = ref(null) onMounted(() => { const options = { // 小数点位 decimalPlaces: 2, // 持续时间 duration: 1.5 } // 累计回款 new CountUp(titleAmountTarget.value, props.data.allAmount, options).start() // 今日新增 new CountUp(tadayAddedTarget.value, props.data.tadayAdded, options).start() // 今日支出 new CountUp(tadayExpendTarget.value, props.data.tadaySub, options).start() // 今日结余 new CountUp(tadayBalanceTarget.value, props.data.tadayAmount, options).start() }) </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
不要忘记在 template 中定义对应的 ref!
# ECharts 使用指南与学习方案
点击查看
安装 ECharts ,我们这里使用 5.3.2 的版本:
npm i --save [email protected]
点击进入 echarts 官网 (opens new window)
参考 基础入门 (opens new window) 完成基本的柱状图渲染。
由基础案例可以,想要利用 ECharts 完成基本的图表渲染,共分为 5 步:
创建
DOM容器,并指定大小(指定ref方便获取)导入
ECharts模块:import * as echarts from 'echarts'1- 利用
echarts.init(target)方法,获取mChart实例:
const target = ref(null) let mChart onMounted(() => { mChart = echarts.init(target.value) })1
2
3
4
5- 利用
构建
options配置对象(echarts渲染的核心,不同的options意味着不同的图表体现 )const options = { // 图表标题配置 title: { // 标题文本 text: 'ECharts 入门示例' }, // 图例配置 legend: { // 图例数据 data: ['销量'] }, // X 轴配置 xAxis: { // 数据 data: ['衬衫', '羊毛衫', '雪纺衫', '裤子', '高跟鞋', '袜子'] }, // Y 轴配置 yAxis: [{}], // 图表类型(可以指定多个) series: [ { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[0] name: '销量', // 图表的类型 type: 'bar', // 图表的数据 data: [5, 20, 36, 10, 10, 20] } ] };1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30最后利用
mChart.setOption方法配置optionsmChart.setOption(options)1最终完整代码为:
<template> <--1.创建DOM容器,并指定大小(指定ref方便获取)--> <div class="trend-chart-container" ref="target"></div> </template> <script setup> // 2.导入ECharts模块: import * as echarts from 'echarts' import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue' // 3.利用echarts.init(target)方法,生成mChart实例 const target = ref(null) let mChart onMounted(() => { mChart = echarts.init(target.value) renderChart() }) /** * 图表渲染方法 */ const renderChart = () => { // 4.创建options配置对象决定echarts最终以什么方式进行呈现 const options = { // 图表标题配置 title: { // 标题文本 text: 'ECharts 入门示例' }, // 图例配置 legend: { // 图例数据 data: ['销量'] }, // X 轴配置 xAxis: { // 数据 data: ['衬衫', '羊毛衫', '雪纺衫', '裤子', '高跟鞋', '袜子'] }, // Y 轴配置 yAxis: [{}], // 图表类型(可以指定多个) series: [ { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[0] name: '销量', // 图表的类型 type: 'bar', // 图表的数据 data: [5, 20, 36, 10, 10, 20] } ] } // 5.利用 mChart.setOption 方法配置 options mChart.setOption(options) } </script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .trend-chart-container { height: 100%; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62对于
ECharts而言,开发流程几乎固定(5 步)渲染图表的关键是
options配置对象配置对象可通过 配置项手册 (opens new window) 进行查看
答:需要经常 参考对照 配置项手册 (opens new window) !
# 累计收益-柱状图与曲线图的混合渲染
接下来我们就通过数据来渲染 累计收益图表
传递数据到
src/views/chart/components/trend/trend-chart.vue中:const props = defineProps({ data: { type: Object, required: true } })1
2
3
4
5
6在
src/views/chart/components/trend/index.vue中完成传递:<trend-chart-vue :data="chartTrendData" />1根据数据构建全新的
options配置对象:const options = { // 鼠标移入之后的提示框配置 tooltip: { // 鼠标移入到坐标轴时,触发提示框 trigger: 'axis', // 移入坐标轴时,提示框的配置项 axisPointer: { // 显示十字准星指示器 type: 'cross', // 指示器样式 crossStyle: { // 色值 color: '#999' } } }, // 图例配置 legend: { // 图例数据 // 右上角数据表示 data: ['月累计收益', '日收益曲线'], // 图例位置 right: 0 }, // echarts 网格绘制的位置,对应 上、右、下、左 grid: { top: 20, right: 0, bottom: 0, left: 0, // 计算边距时,包含标签 containLabel: true }, // X 轴配置 xAxis: { // 坐标轴类型,category:类目轴 type: 'category', // 坐标轴数据 data: props.data.monthAmountList.map(item => item.time), // 刻度尺配置 axisTick: { // 不显示坐标轴刻度 show: false } }, // y 轴配置 yAxis: { // Y 轴类型,value:数值轴 type: 'value', // 最小值 min: 0, // 最大值 max: function(value) { // 取整 return parseInt(value.max * 1.2) }, // 刻度上展示的文字 axisLabel: { formatter: '{value} 万元' } }, // 图表类型 // 鼠标移入显示的数据 series: [ // 第一个图表 { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[0] name: '月累计收益', // 图表类型 type: 'bar', // 柱的宽度 barWidth: 20, // 提示框展示配置 tooltip: { // 提示框展示的内容 valueFormatter: function(value) { return value + '万元' } }, // 数据源 data: props.data.monthAmountList.map(item => item.amount) }, // 第二个图表 { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[1] name: '日收益曲线', // 图表类型 type: 'line', // 颜色 color: '#6EC6D0', // 平滑 smooth: true, // 提示框展示配置 tooltip: { // 提示框展示的内容 valueFormatter: function(value) { return value + '万元' } }, // 数据源 data: props.data.dailyCurve.map(item => item.amount) } ] }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
# 累计收益-混合图表的国际化处理
最后对于累计收益模块,我们需要处理 混合图表的国际化展示。
我们知道,想要国际化的处理其实被分为两种情况:
- 在
template中,利用$t方法处理国际化。这种情况下,当我们切换locale的时候,内容会自动重新渲染。就像在trend-data时一样。 - 在
script中,利用i18n.t方法处理国际化。在这种情况下,当我们切换locale的时候,需要通过watchSwitchLang方法,监听语言变化,再利用i18n.t重新获取最新的语言内容才可以。
那么我们当前就处于 场景二 之中。
生成
i18n实例:import { useI18n } from 'vue-i18n' const i18n = useI18n()1
2
3修改固定文本为
i18n.t方法:const options = { ... // 图例配置 legend: { // 图例数据 data: [i18n.t('msg.chart.monthIncome'), i18n.t('msg.chart.dayIncome')], ... }, ... // y 轴配置 yAxis: { ... // 刻度上展示的文字 axisLabel: { formatter: `{value} ${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')}` } }, // 图表类型 series: [ // 第一个图表 { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[0] name: i18n.t('msg.chart.monthIncome'), ... tooltip: { // 提示框展示的内容 valueFormatter: function(value) { return value + i18n.t('msg.chart.unit') } }, ... }, // 第一个图表 { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[1] name: i18n.t('msg.chart.dayIncome'), ... tooltip: { // 提示框展示的内容 valueFormatter: function(value) { return value + i18n.t('msg.chart.unit') } }, ... } ] }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47最后通过
watchSwitchLang方法,重新触发renderChart:import { watchSwitchLang } from '@/utils/i18n' watchSwitchLang(renderChart)1
2
3
# 日历模块-日历数据基础渲染
在 src/views/chart/components/calendar/index.vue 中,利用 element-plus 的 calendar (opens new window) 组件完成日历基本渲染:
点击查看
<template>
<el-card
class="container"
:body-style="{
padding: 0
}"
>
<el-calendar class="calendar" v-model="currentDate">
<!--命名插槽-->
<template #dateCell="{ data }">
<!-- 展示的内容 -->
<p :class="[data.isSelected ? 'is-selected' : '']">
<!-- 显示的内容 -->
{{
data.day
.split('-')
.slice(2)
.join('')
}}
<br />
</p>
</template>
</el-calendar>
</el-card>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 选中的日期
const currentDate = ref(new Date())
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.container {
height: 443px;
.calendar {
::v-deep .el-calendar__body {
padding: 0 12px 12px;
font-size: 14px;
}
::v-deep .el-calendar-day {
height: 66px !important;
padding: 0 !important;
p {
height: 100%;
padding: 8px;
}
// 金额样式
.amount {
font-size: 12px;
}
// 正收益
.profit {
background-color: #f3fff3;
span {
color: #649840;
}
}
// 负收益
.loss {
background-color: #ffe7e7;
span {
color: #b65d59;
}
}
.is-selected {
background-color: #d6f2ff;
}
}
}
}
</style>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
# 日历模块-定制数据可视化处理
在
src/api/chart.js中定义日历图示数据接口:/** * 日历图示数据 */ export const getChartCalendar = () => { return request({ url: '/chart/calendar' }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8在
src/views/chart/components/calendar/index.vue中获取数据:<script setup> import { ref } from 'vue' import { getChartCalendar } from '@/api/chart' /** * 获取数据 */ const calendarListData = ref([]) const getCalendarListData = async () => { const { result } = await getChartCalendar() calendarListData.value = result } getCalendarListData() </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14创建方法
getTadayAmount,用于:返回指定日期收益数据,在日历中进行展示:/** * 返回指定日期收益数据,在日历中进行展示 */ const getTadayAmount = date => { // 根据日期,获取当日数据 const tadayData = calendarListData.value.find(item => item.date === date) // 判断当日数据是否存在 if (!tadayData) { return 0 } // 获取当日收益 const tadayAmount = tadayData.amount return tadayAmount }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14在
template中,添加当日金额视图:<template #dateCell="{ data }"> <p :class="[data.isSelected ? 'is-selected' : '']"> <!-- 显示的内容 --> ... <br /> <!-- 当日金额 --> <span class="amount" v-if="getTadayAmount(data.day)"> {{ getTadayAmount(data.day) }} </span> </p> </template>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11为避免
getTadayAmount被多次计算,创建简单的缓存处理:// 收益缓存数据。 // key 为日期 // val 为对应的 金额 const dateAmountList = ref({}) /** * 返回指定日期收益数据,在日历中进行展示 */ const getTadayAmount = date => { // 读取缓存数据 if (dateAmountList.value[date]) { return dateAmountList.value[date] } ... // 对数据进行缓存 dateAmountList.value[date] = tadayAmount return tadayAmount }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19至此,日历中可展示每日金额收益
最后我们期望为 正收益添加
profit样式,为 负收益添加loss样式创建
calendarItemBgClass方法,处理对应样式行为:/** * 返回日历的背景 * */ const calendarItemBgClass = day => { if (getTadayAmount(day) > 0) { return 'profit' } else if (getTadayAmount(day) < 0) { return 'loss' } return '' }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11在
template中使用此方法:<template #dateCell="{ data }"> <p :class="[ data.isSelected ? 'is-selected' : '', + calendarItemBgClass(data.day) ]" >1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 日金额分析-横向与负坐标图表构建
对于该模块而言,同样以 柱状图 的形式呈现,然而不同的是,它是一个横向的,并且具备负数。
所以说在本小节中我们需要构建一个 横向,包含负数的柱状图。以此对比 累计收益 的柱状图,相信可以让大家对 ECharts 的图表绘制有更深的理解。
在
src/api/chart.js中创建数据获取方法:/** * 指定日期的时段柱形数据 */ export const getChartTimeAmount = date => { return request({ url: '/chart/time/amount', params: { date } }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11在
src/views/chart/components/horizontal-bar/index.vue中获取接口数据:<script setup> import { getChartTimeAmount } from '@/api/chart' import { ref } from 'vue' /** * 获取数据 */ const data = ref([]) const getData = async date => { const { result } = await getChartTimeAmount(date) data.value = result // 渲染图表 renderChart() } getData() </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16根据数据绘制图表,同时处理国际化内容:
<script setup> import { getChartTimeAmount } from '@/api/chart' import * as echarts from 'echarts' import { onMounted, ref } from 'vue' // 国际化相关 import { useI18n } from 'vue-i18n' import { watchSwitchLang } from '@/utils/i18n' const i18n = useI18n() ... /** * 图表初始化 */ const target = ref(null) let mChart = null onMounted(() => { mChart = echarts.init(target.value) }) /** * 构建图表 */ const renderChart = () => { const options = { // 鼠标移入之后的提示框配置 tooltip: { // 鼠标移入到坐标轴时,触发提示框 trigger: 'axis', // 移入坐标轴时,提示框的配置项 axisPointer: { // 指示器展示阴影 type: 'shadow' } }, // 图例配置 legend: { // 图例数据 data: [ `${i18n.t('msg.chart.income')}(${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')})`, `${i18n.t('msg.chart.expend')}(${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')})`, `${i18n.t('msg.chart.balance')}(${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')})` ], // 图例位置 right: 0 }, // echarts 网格绘制的位置,对应 上、右、下、左 grid: { top: 28, right: 0, bottom: 0, left: 0, // 计算边距时,包含标签 containLabel: true }, // X 轴配置 xAxis: [ { // 数值轴,适用于连续数据 type: 'value' } ], // y 轴配置 yAxis: [ { // 坐标轴类型,category:类目轴 type: 'category', // 刻度尺配置 axisTick: { // 不显示坐标轴刻度 show: false }, // Y 轴数据 data: data.value.map(item => item.timeStr), // 反向展示 inverse: true } ], // 图表类型 series: [ // 第一个图表:收益 { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[0] name: `${i18n.t('msg.chart.income')}(${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')})`, // 图表类型 type: 'bar', // 数据堆叠,两个相同的 stack 将会堆叠渲染 stack: 'Total', // 标签配置 label: { // 展示 show: true, // 右侧 position: 'right' }, // 柱的颜色 color: '#6DC473', // 高亮配置 emphasis: { // 聚焦当前高亮的数据所在的系列的所有图形 focus: 'series' }, // 数据 data: data.value.map(item => item.income) }, // 第二个图表:支出 { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[1] name: `${i18n.t('msg.chart.expend')}(${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')})`, // 图表类型 type: 'bar', // 数据堆叠,两个相同的 stack 将会堆叠渲染 stack: 'Total', // 标签配置 label: { // 展示 show: true, // 右侧 position: 'right' }, // 柱的颜色 color: '#E47470', // 高亮配置 emphasis: { // 聚焦当前高亮的数据所在的系列的所有图形 focus: 'series' }, // 数据 data: data.value.map(item => item.expense) }, // 第三个图表:结余 { // 图表名字,对应 legend.data[2] name: `${i18n.t('msg.chart.balance')}(${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')})`, // 图表类型 type: 'bar', // 标签配置 label: { // 展示 show: true, // 内部 position: 'inside' }, // 柱的颜色 color: '#83C0DF', // 高亮配置 emphasis: { // 聚焦当前高亮的数据所在的系列的所有图形 focus: 'series' }, // 数据 data: data.value.map(item => item.balance) } ] } mChart.setOption(options) } watchSwitchLang(renderChart) </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160最后对样式进行修正:
<template> <el-card :body-style="{ paddingTop: '12px' }" > <div class="container" ref="target"></div> </el-card> </template> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { height: 403px; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 非父子组件之间进行交互的三种方式
在 Vue 的项目中,涉及到组件之间通讯,通常会有两种场景:
- 父子组件通讯:这也是我们最常见的一种场景,可以通过
props或emits来完成。 - 非父子组件通讯:这种情况相对比较复杂,因为两个无关的组件进行通讯必须要找到一个 “沟通者” ,这个沟通者必须可以与双方都进行通讯。通常情况下有三种方式:
- 找到双方共同的父组件:通过子向父通讯,父向子通讯的方式
- 优点:以现有技术即可完成
- 缺点:大量的跨组件处理事件,会导致逻辑变得非常复杂,各个组件之间的耦合性变强
- 借助
vuex:因为vuex是可以与所有组件都进行交互的,所以可以借助它承担 “沟通者” 的角色- 优点:以现有技术即可完成
- 缺点:数据必须由
Vuex处理,如果该数据之前没有存放在Vuex中,则需要进行较大的改动
- 事件中心
EventHub:所谓事件中心其实就有一个 公开的单例,一般会提供emits 发送事件和on 监听事件两个方法。在Vue2中vm实例因为直接具备这两个方法,所以可以直接作为事件中心实例。而在Vue3中,取消了on方法,所以如果想要实现这种机制,则需要通过 mitt (opens new window) 来进行实现。- 优点:有利于组件之间的解耦,增加可维护性
- 缺点:当事件足够多时,会导致事件中心极其复杂
- 找到双方共同的父组件:通过子向父通讯,父向子通讯的方式
那么综上所述,我们可知:如果只是进行少量的非父子组件通讯,那么通过 EventHub 的形式处理 是比较好的。
# 跨组件通讯-日历图与柱状图联动处理
-
npm i --save [email protected]1 创建
src/utils/eventHub.js,作为事件中心:import mitt from 'mitt' /** * 注意: * 这种方式在 Vue3 中,已经没有原生的实现,可以借助 mitt 进行实现。但是这种方式并不适合大范围的使用,因为很有可能会导致出现事件紊乱的错误。 */ export default mitt()1
2
3
4
5
6
7在
src/views/chart/components/calendar/index.vue中,监听currentDate的变化,发送事件:import emitter from '@/utils/eventHub' // 选中的日期 const currentDate = ref(new Date()) /** * 触发日期改变的事件 */ watch(currentDate, val => { emitter.emit('calendarChange', val) })1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10在
src/views/chart/components/horizontal-bar/index.vue中,通过on方法监听事件:import emitter from '@/utils/eventHub' /** * 与日历图联通 */ emitter.on('calendarChange', val => { getData(val) })1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 大区营销-饼图图表构建
在
src/api/chart.js中定义数据接口:/** * 饼图数据 */ export const getChartPie = () => { return request({ url: '/chart/pie' }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8在
src/views/chart/components/pie/index.vue中通过接口获取数据:<script setup> import { ref } from 'vue' import { getChartPie } from '@/api/chart' const chartData = ref([]) const getChartData = async () => { const res = await getChartPie() chartData.value = res // 渲染图表 } getChartData() </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12构建基础的
html:<template> <el-card :body-style="{ padding: 0 }" > <div ref="target" class="container"></div> </el-card> </template> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { height: 240px; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15渲染图表,并处理国际化内容:
<script setup> import { onMounted, ref } from 'vue' import * as echarts from 'echarts' import { getChartPie } from '@/api/chart' import { useI18n } from 'vue-i18n' import { watchSwitchLang } from '@/utils/i18n' const i18n = useI18n() ... const target = ref(null) let mChart = null onMounted(() => { mChart = echarts.init(target.value) }) const renderChart = () => { const options = { // 标题 title: { text: i18n.t('msg.chart.pieChartTitle') }, // 鼠标移入的提示 tooltip: { trigger: 'item', // {b}:数据名。{c}:数值。 formatter: `{b}: {c} ${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')}` }, series: [ { // 饼图 type: 'pie', // 饼图的半径。第一项为内半径,第二项为外半径 radius: ['40%', '70%'], // 每个 item 的样式 itemStyle: { // 圆角 borderRadius: 10, // 边框色 borderColor: '#fff', // 边框宽度 borderWidth: 2 }, // 文字 label: { // 默认不显示 show: false, // {b}:数据名。{d}:百分比。 formatter: '{b}: {d}%', // 居中展示(在鼠标移入时) position: 'center' }, // 高亮状态的扇区和标签样式 emphasis: { // 文本 label: { show: true, fontSize: '22', fontWeight: 'bold' } }, data: chartData.value } ] } mChart.setOption(options) } watchSwitchLang(renderChart) </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
# 文档云图-WordCloud 基础渲染
对于 ECharts 而言,默认并没有提供文档云图的图表渲染,如果我们想要渲染文档云图的话,那么需要借助另外一个包:echarts-wordcloud (opens new window)
对于该包的使用非常简单,只需要在需要渲染文档云图时,指定:import 'echarts-wordcloud'; 导入即可。
安装
echarts-wordcloud:npm install [email protected]1定义文档云图数据接口:
/** * 文字云图数据 */ export const getChartWordCloud = () => { return request({ url: '/chart/wordcloud' }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8在
src/views/chart/components/word-cloud/index.vue中获取数据:/** * 获取数据 */ const wordCloudData = ref([]) const getWordCloudData = async () => { const res = await getChartWordCloud() wordCloudData.value = res // 渲染图表 } getWordCloudData()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10构建基本的
html和css:<template> <el-card :body-style="{ padding: 0 }" > <div class="container" ref="target"></div> </el-card> </template> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { height: 240px; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15渲染图表:
<script setup> import * as echarts from 'echarts' import 'echarts-wordcloud' import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue' import { randomRGB } from '@/utils/color' import { getChartWordCloud } from '@/api/chart.js' import { useI18n } from 'vue-i18n' import { watchSwitchLang } from '@/utils/i18n' const i18n = useI18n() ... const target = ref(null) let mChart = null onMounted(() => { mChart = echarts.init(target.value) }) /** * 渲染图表 */ const renderChart = () => { var option = { title: { text: i18n.t('msg.chart.cloudChartTitle') }, series: [ { // 类型 type: 'wordCloud', // 数据映射文本的大小范围 sizeRange: [4, 80], // 文字旋转范围 rotationRange: [0, 0], // 单词之间的间距 gridSize: 0, // 渲染动画 layoutAnimation: true, // 字体 textStyle: { // 随机色值 color: randomRGB }, // 高亮字体 emphasis: { textStyle: { fontWeight: 'bold', color: '#000' } }, // 数据 data: wordCloudData.value } ] } mChart.setOption(option) } watchSwitchLang(renderChart) </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62创建
src/utils/color.js,暴露randomRGB方法:/** * 生成随机色值 */ export const randomRGB = () => { const r = Math.floor(Math.random() * 255) const g = Math.floor(Math.random() * 255) const b = Math.floor(Math.random() * 255) return `rgb(${r}, ${g}, ${b})` }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 文档云图-基于图形轮廓的绘制
期望它能够:在绘制文档的同时,预留出 imooc 的一个 logo 图形
需要借助 wordCloud 的 maskImage 属性,通过该属性指定图形轮廓。
在
renderChart中,构建img实例:import wordcloudBg from '@/assets/wordcloud.png' // 图像轮廓 var maskImage = new Image() maskImage.src = wordcloudBg1
2
3
4
5在
series配置属性中,指定maskImage:// 绘制将排除图像的轮廓 maskImage: maskImage,1
2等待图像加载完成之后,再设置
Option:// 等待图像加载完成之后 maskImage.onload = function() { mChart.setOption(option) }1
2
3
4
# 地图可视化:百度地图 API 大解析
对于地图可视化而言,我们将使用百度地图结合 ECharts 进行绘制。
所以说想要完成地图可视化,首先我们需要:申请百度地图应用:
点击查看
# 注册开发者
- 打开 百度地图 API (opens new window)
- 点击右上角登录按钮:
- 选择立即注册(百度系账号通用):
- 账号注册成功之后,重新进入 百度地图 API (opens new window) 平台
- 点击控制台,注册称为开发者:
- 咱们这里选择 个人开发者:
- 填写开发者信息:
- 完善基本信息:
- 上传身份证信息:
- 注册成功之后,个人开发者应该是即时就可以生效的。
# 申请应用
- 登录账号之后,点击控制台,此时可以进入控制台页面
- 点击 应用管理 -> 我的应用 ,选择 创建应用
- 填入基本应用信息,重点:注意
Referer白名单,因为这个应用可能会被很多同学使用,所以我们填写的是*! - 点击提交,应用创建完成,此时我们可以得到一个
访问应用(AK)
# 地图可视化:百度地图 + ECharts 完成可视化渲染
需要结合 百度地图 和 ECharts 的 bmap.js 模块才可以。
在
public/index.html中,导入百度地图API(通用AK:Lw93eLNTRghjevtCP8rgYDqkMtcw4zU3):<script src="https://api.map.baidu.com/api?v=3.0&ak=${此处写入你的 AK }"></script>1在
src/api/chart.js中,定义地图可视化数据接口:/** * 地图可视化 */ export const getChartMap = () => { return request({ url: '/chart/bmap' }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8在
src/views/chart/components/b-map/index.vue中,获取对应数据:/** * 获取数据 */ const chartData = ref({}) const getChartData = async () => { const res = await getChartMap() chartData.value = res // 渲染图表 } getChartData()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10注意: 此时服务端返回的数据包含两个属性:
data:所有的城市和对应数据geoCoordMap:所有城市和对应坐标
该数据是 不可以 直接在地图可视化中进行渲染的,所以我们需要对该数据进行 重置:
期望重置为该格式数据:
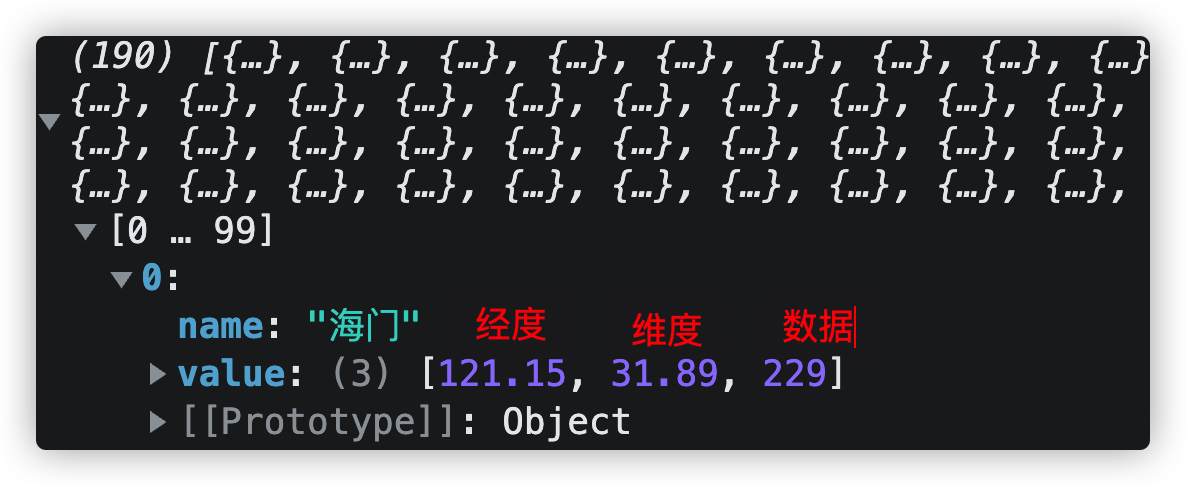
所以得出以下算法:
/** * 数据转化方法 */ const convertData = function (data) { // 返回值 const res = [] // 遍历所有城市数据 data.forEach((item) => { // 根据城市名从 geoCoordMap 中获取对应坐标 const geoCoord = chartData.value.geoCoordMap[item.name] // 如果可以获取到坐标,则生成新的数据对象 if (geoCoord) { // 该数据对象为: // name:城市名 // value:数组[经度、维度、数据] res.push({ name: item.name, value: [...geoCoord, item.value] }) } }) return res }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23构建
HTML和CSS结构:点击查看
<template> <el-card class="container" > <div class="title">{{ $t('msg.chart.bmapChartTitle') }}</div> <div ref="target" class="box"></div> </el-card> </template> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { position: relative; .title { position: absolute; top: 28px; margin-left: 50%; transform: translateX(-50%); color: #333; font-size: 22px; font-weight: bold; z-index: 9; } .box { height: 462px; } } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27导入
ECharts中处理地图模块bmap:// 导入 bmap 模块 import 'echarts/extension/bmap/bmap.js'1
2完成图表渲染:
const i18n = useI18n() /** * 初始化 echarts */ const target = ref(null) let mChart = null onMounted(() => { mChart = echarts.init(target.value) }) /** * 渲染地图数据 */ const renderBMap = () => { const options = { tooltip: { trigger: 'item' }, // 地图配置 bmap: { // 中心点 center: [109.114129, 36.550339], // 缩放级别 zoom: 5, // 是否可拖动 roam: true }, series: [ { name: `营收(${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')})`, // 散点图 type: 'scatter', // 使用的表坐标 coordinateSystem: 'bmap', // 数据源 data: convertData(chartData.value.data), // 散点的大小 symbolSize: function (val) { return val[2] / 10 }, // 数据使用下标为2的值(item.value[2]) encode: { value: 2 }, // 鼠标移入时,高亮的标签样式 emphasis: { label: { // 鼠标移入时,显示高亮 show: true } }, // 散点色值 color: '#15803d' }, { name: `营收 TOP 5(${i18n.t('msg.chart.unit')})`, // 包含涟漪特效动画的散点的散点图 type: 'effectScatter', // 使用的表坐标 coordinateSystem: 'bmap', // 数据源(top 5) data: convertData( chartData.value.data .sort(function (a, b) { return b.value - a.value }) .slice(0, 6) ), // 散点的大小 symbolSize: function (val) { return val[2] / 10 }, // 数据使用下标为2的值(item.value[2]) encode: { value: 2 }, // 涟漪特效 rippleEffect: { // stroke 类型的波纹 brushType: 'stroke' }, // 显示地名 label: { formatter: '{b}', position: 'right', show: true }, // 散点层级 zlevel: 2, // 散点色值 color: '#166534' } ] } mChart.setOption(options) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
# 大区营销数据分析-基础结构渲染
点击查看
创建
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/components/s2.vue作为图表渲染组件<template> <el-card :body-style="{ padding: 0 }" > <div class="container" ref="target">s2</div> </el-card> </template> <script setup></script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { height: 782px; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17创建
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/components/sheet-label.vue作为大区渲染组件<template> <el-card :body-style="{ padding: 0 }" > <div class="container">sheet-label</div> </el-card> </template> <script setup></script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { height: 112px; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/index.vue中,渲染对应结构:<template> <el-row :gutter="20"> <el-col :span="18"> <s2Vue /> </el-col> <el-col :span="6"> <sheetLabelVue v-for="item in 6" :key="item" class="mb-20" /> </el-col> </el-row> </template> <script setup> import s2Vue from './components/s2.vue' import sheetLabelVue from './components/sheet-label.vue' </script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .mb-20 { margin-bottom: 20px; } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 大区营销数据分析-渲染大区结构视图
本小节我们来渲染右侧大区结构视图。
点击查看
在
src/api/chart.js中定义大区数据获取接口:/** * 大区数据 */ export const getChartRegions = () => { return request({ url: '/chart/regions' }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/index.vue中获取数据,渲染视图:import { getChartRegions } from '@/api/chart' import { ref } from 'vue' import { watchSwitchLang } from '@/utils/i18n' /** * 获取大区数据 */ const regionsData = ref([]) const getChartRegionsData = async () => { const { regions } = await getChartRegions() regionsData.value = regions // TODO:获取该大区对应的数据 } getChartRegionsData() // 切换语言,数据重新获取 watchSwitchLang(getChartRegionsData)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16<sheetLabelVue :data="item" v-for="item in regionsData" :key="item.id" class="mb-20" />1
2
3
4
5
6在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/components/sheet-label.vue中渲染数据:<template> <el-card class="mb-20" :body-style="{ padding: 0 }" > <div class="container"> <p class="title">{{ data.title }}</p> <div class="desc"> <span>{{ $t('msg.chart.tadayReceivable') }}</span> <p class="profit"> ¥ {{ data.receivable }} <span class="unit">({{ $t('msg.chart.unit') }})</span> </p> </div> <div class="desc"> <span>{{ $t('msg.chart.tadayBalance') }}</span> <p :class="data.balance > 0 ? 'profit' : 'loss'"> ¥ {{ data.balance }} <span class="unit">({{ $t('msg.chart.unit') }})</span> </p> </div> </div> </el-card> </template> <script setup> import { defineProps } from 'vue' defineProps({ // 数据源 data: { type: Object, required: true } }) </script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { padding: 20px; border-radius: 5px; background-color: #f2f3f9; cursor: pointer; .title { font-size: 18px; font-weight: bold; margin-bottom: 8px; } .desc { font-size: 12px; margin-top: 6px; color: #999; display: flex; justify-content: space-between; } .unit { color: #999; } .profit { color: #649840; } .loss { color: #b65d59; } } </style>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72基本视图渲染完成
接下来处理高亮点击行为
在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/components/sheet-label.vue中定义:defineProps({ // 是否被选中 isSelected: { type: Boolean }, ... })1
2
3
4
5
6
7<div class="container " :class="{ selected: isSelected }">1.selected { border-left: 6px solid #5172e9; background-color: white; }1
2
3
4在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/index.vue中,定义选中数据:<template> ... <sheetLabelVue :isSelected="currentRegionsIndex === index" @click="onChangeRegion(index)" ... /> ... </template> <script setup> ... /** * 获取大区数据 */ const currentRegionsIndex = ref(0) ... /** * 切换大区 */ const onChangeRegion = (index) => { currentRegionsIndex.value = index // TODO:获取该大区对应的数据 } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 大区营销数据分析-基于 AntV S2 构建表格数据可视化
接下来我们将基于 AntV S2 模块 (opens new window) 来实现我们的表格数据可视化逻辑。
首先安装
@antv/s2到项目中:npm i --save @antv/[email protected]1s2的使用整体分为 6 步:- 按需导入
TableSheet模块 - 创建
DOM作为渲染的容器,并且需要指定宽高 - 构建 S2DataConfig (opens new window) 对象,为表的数据源
- 构建 S2Options (opens new window) 对象,为表的配置对象
- 生成 TableSheet (opens new window) 实例,得到
S2 - 触发
s2.render()方法,完成表的渲染
- 按需导入
# 基础渲染
在
src/api/chart.js中,定义数据接口:/** * 表格数据 */ export const getChartSheet = regionId => { return request({ url: '/chart/sheets', params: { regionId } }) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/index.vue获取对应数据:import { getChartSheet } from '@/api/chart' /** * 大区对应的表格数据 */ const sheetData = ref([]) const getChartSheetData = async id => { const res = await getChartSheet(id) sheetData.value = res } getChartSheetData()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/components/s2.vue中定义props接收数据:const props = defineProps({ data: { type: Array, required: true } })1
2
3
4
5
6在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/index.vue中传递数据:<s2Vue :data="sheetData" />1在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/components/s2.vue中获取指定DOM,并生成s2实例:<script setup> import { ref, watch, defineProps, onMounted } from 'vue' import { TableSheet } from '@antv/s2' import { useI18n } from 'vue-i18n' const i18n = useI18n() const props = defineProps({ data: { type: Array, required: true } }) const target = ref(null) let s2 = null onMounted(() => { // 数据对象 const s2DataCfg = { fields: { columns: [ 'province', 'city', 'coverage', 'receivable', 'actual', 'balance' ] }, meta: [ // 列头字段对应的元信息,比如展示的中文名 { field: 'province', name: i18n.t('msg.chart.sheetProvince') }, { field: 'city', name: i18n.t('msg.chart.sheetCity') }, { field: 'coverage', name: i18n.t('msg.chart.sheetCoverage') }, { field: 'receivable', name: i18n.t('msg.chart.sheetReceivable') }, { field: 'actual', name: i18n.t('msg.chart.sheetActual') }, { field: 'balance', name: i18n.t('msg.chart.sheetBalance') } ], data: props.data } // 配置对象 const s2Options = { // 宽度:必须为准确的像素 width: target.value.clientWidth, // 高度:必须为准确的像素 height: target.value.clientHeight, // 是否显示行序号 showSeriesNumber: true, // 条件模式配置 conditions: { // 背景字段标记 background: [ { // 设置背景的字段 field: 'balance', // 映射函数 mapping(fieldValue) { console.log(fieldValue) return { fill: fieldValue > 0 ? '#f3fff3' : '#ffe7e7' } } } ] } } // 生成 S2 实例 s2 = new TableSheet(target.value, s2DataCfg, s2Options) // 渲染视图 s2.render(true) }) </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
# 大区营销数据分析-表格图谱与大区联动
当表格渲染成功之后,下面我们要处理表格和大区的联动,我们期望,当切换不同大区时,表格的数据可以切换展示。
在大区数据获取完成后,触发
getChartSheetData方法:const getChartRegionsData = async () => { ... // TODO:获取该大区对应的数据 getChartSheetData(regionsData.value[0].id) }1
2
3
4
5在
onChangeRegion切换大区时,重新触发getChartSheetData方法:/** * 切换大区 */ const onChangeRegion = (index) => { currentRegionsIndex.value = index // TODO:获取该大区对应的数据 + getChartSheetData(regionsData.value[index].id) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8在
src/views/chart/components/table-sheet/components/s2.vue中,监听data的变化,触发render函数:onMounted(() => { // 配置对象 const s2Options = { ... } // 生成 S2 实例,数据对象置为 null s2 = new TableSheet(target.value, {}, s2Options) }) /** * 图标渲染函数 */ const renderChart = () => { // 数据对象 const s2DataCfg = { ... } // 更新数据 s2.setDataCfg(s2DataCfg) // 渲染视图,传入 true 表示数据发生了更新 s2.render(true) } /** * 监听数据变化 */ watch( () => props.data, () => { renderChart() } )1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33此时,表格与大区联动完成。
最后处理下国际化内容:
/** * 监听语言变化 */ watchSwitchLang(renderChart)1
2
3
4
# 总结
新增的加餐内容,并没有提供 大屏可视化 的对应内容,因为就像我们之前所说的 大屏可视化 主要以单独的项目进行展示,并不适合集成到后台解决方案之中。另外,也是最重要的一点:大屏可视化与数据可视化在解决方案中,并没有本质的区别。